Universal Remote - Part IV
With the hardware built the next step is getting the Raspberry Pi up and running and installing LIRC. Alexba.in has a comprehensive post for both of these things: RaspberryPi Quickstart and Setting Up LIRC on the RaspberryPi.
I discovered and modified a few things along the way, so here’s what I did:
- Download the latest Raspbian Image and follow their Installation Guide.
- Network the Pi over wired Ethernet using RJ45 connector.
- Connect to the Pi over SSH with PuTTy.
Since I’d like to connect over WiFi I’ve added a Belkin USB F7D2101. For future development, I also added a ORICO BTA-402 USB Bluetooth 4.0 Micro Adapter Dongle for controlling a Play Station 3 using GIMX.
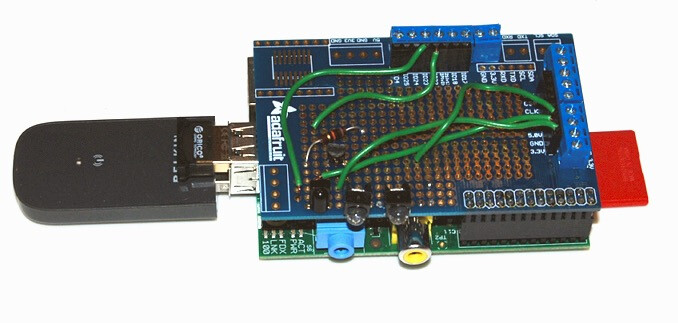
-
With the Pi temporarily connected by Ethernet cable, I set up the wireless connection via the command line over SSH.
-
The following commands update the Software and Firmware then sync the Time with a source on the Internet:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
sudo apt-get install git-core
sudo wget http://goo.gl/1BOfJ -O /usr/bin/rpi-update && sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/rpi-update
sudo rpi-update
sudo apt-get install ntpdate
sudo ntpdate -u ntp.ubuntu.com
- Next install LIRC
sudo apt-get install lirc
- Modify /etc/modules and /etc/lirc/hardware.conf for the specific hardware being used:
/etc/modules
lirc_dev
lirc_rpi gpio_in_pin=23 gpio_out_pin=22
/etc/lirc/hardware.conf
######################
# /etc/lirc/hardware.conf
#
# Arguments which will be used when launching lircd
LIRCD_ARGS="--uinput"
# Don't start lircmd even if there seems to be a good config file
# START_LIRCMD=false
# Don't start irexec, even if a good config file seems to exist.
# START_IREXEC=false
# Try to load appropriate kernel modules LOAD_MODULES=true
# Run "lircd --driver=help" for a list of supported drivers.
DRIVER="default"
# usually /dev/lirc0 is the correct setting for systems using udev
DEVICE="/dev/lirc0"
MODULES="lirc_rpi"
# Default configuration files for your hardware if any
LIRCD_CONF="" LIRCMD_CONF=""
######################
- Restart LIRC to pick up these changes:
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc stop
mode2 -d /dev/lirc0
- Pressing buttons on an IR remote pointed at the receiver and activity similar to the following should be displayed:
space 16300
pulse 95
space 28794
pulse 80
space 19395
pulse 83
In the next post on this topic I’ll cover recording the IR signal from remotes using the irrecord command and testing functionality from the command line. I’ll also install Node.js and the client library lirc_node for controlling LIRC from a web site.